In the middle-part of the 18th century, the art world ditched the gaudy baroque style and went back to the classics. This period (and style) is known as Neoclassicism; or Neoclassical art. But what is Neoclassicism really? We’re going to break down Neoclassicism by looking at its history, with examples from Jacques-Louis David, Angelica Kauffmann, and more. By the end, you’ll know how Neoclassicism began, and why it’s influenced artists around the world for hundreds of years.
What is Neoclassicism?
First, let’s define Neoclassicism
Neoclassicism is an important style to understand for writers, filmmakers, artists, and architects. Why? Because it changes how we think about classical art. And not just classical art as in “Greek and Roman art” but all art that we consider classical. For more, check out our index of art styles covering more specific and noteworthy movements.
For more on the basic ideas behind Neoclassicism, check out this quick video from Phil Hansen.
What is Neoclassicism? • Neoclassicism Art – Overview from Phil Hansen
We’re going to cover some Neoclassicism examples in a bit, but first let’s quickly define Neoclassicism.
NEOCLASSICISM DEFINITION
What is Neoclassicism?
Neoclassicism was an art movement that sought to evoke the style of classical antiquity in writing, painting, sculpting, and architecture found in Greek and Roman culture. Neoclassicism was most popular between the late 18th century and early 19th century. But its influence still reverberates throughout the art world today.
Popular Neoclassical Artists & Famous Works
- Jacques-Louis David – Oath of the Horatii (1784), The Death of Socrates (1787), and The Lictors Bring to Brutus the Bodies of His Sons (1789).
- Antonio Canova – Theseus and the Minotaur (1781-1782), Venus Victrix (1808), The Three Graces (1814-1817).
- Angelica Kauffmann – Portrait of Winckelmann (1764), Self-portrait (1770-1775), Telemachus and the Nymphs of Calypso (1782).
The Neoclassicism Era Explained
When did Neoclassicism start?
Neoclassicism took off around 1760 due to a growing dissatisfaction with the gaudy baroque art style and the emergence of archaeological findings by German pioneer Johann Joachim Winckelmann.
Let’s break down these two points in further detail.
First: the death of the baroque art style. The baroque art style was founded to contrast classical antiquity. Classical art was simple and sleek; baroque art was intricate and ostentatious.
Here’s a quick history of the baroque style from Phil Hansen.
Before the Neoclassicism Time Period • Baroque Overview by Phil Hansen
The baroque era served an important role in art history, but over time, people got tired of the style and figured, “why not go back to the classics?”
Second: archeological discoveries. German historian Johann Joachim Winckelmann did more to advance Neoclassicism than perhaps anybody else. Not through his own artwork, but through his discovery of ancient art and architecture. Here’s a video on Winckelmann from Accessible Art History.
What is Neoclassicism? • Founders of Art History: Johann Joachim Winckelmann
Winckelmann revealed the discovery of Pompeii to the masses — and the people loved it. In fact, they loved it so much that they wondered why settlements two millennia old looked better than the ones they currently lived in. So, they pushed for a return to classical antiquity, and thus the Neoclassical era was born.
Neoclassicism Artists
Most famous Neoclassical artists
There aren’t many Neoclassical artists with the name cache of Da Vinci or Caravaggio. But that doesn’t mean there aren’t a lot of great Neoclassical artists. Quite the contrary, in fact, many of the most famous Neoclassical artists are regarded as preeminent leaders of their era.
Let’s take a look at a few of the most famous neoclassical artists.
Jacques-Louis David
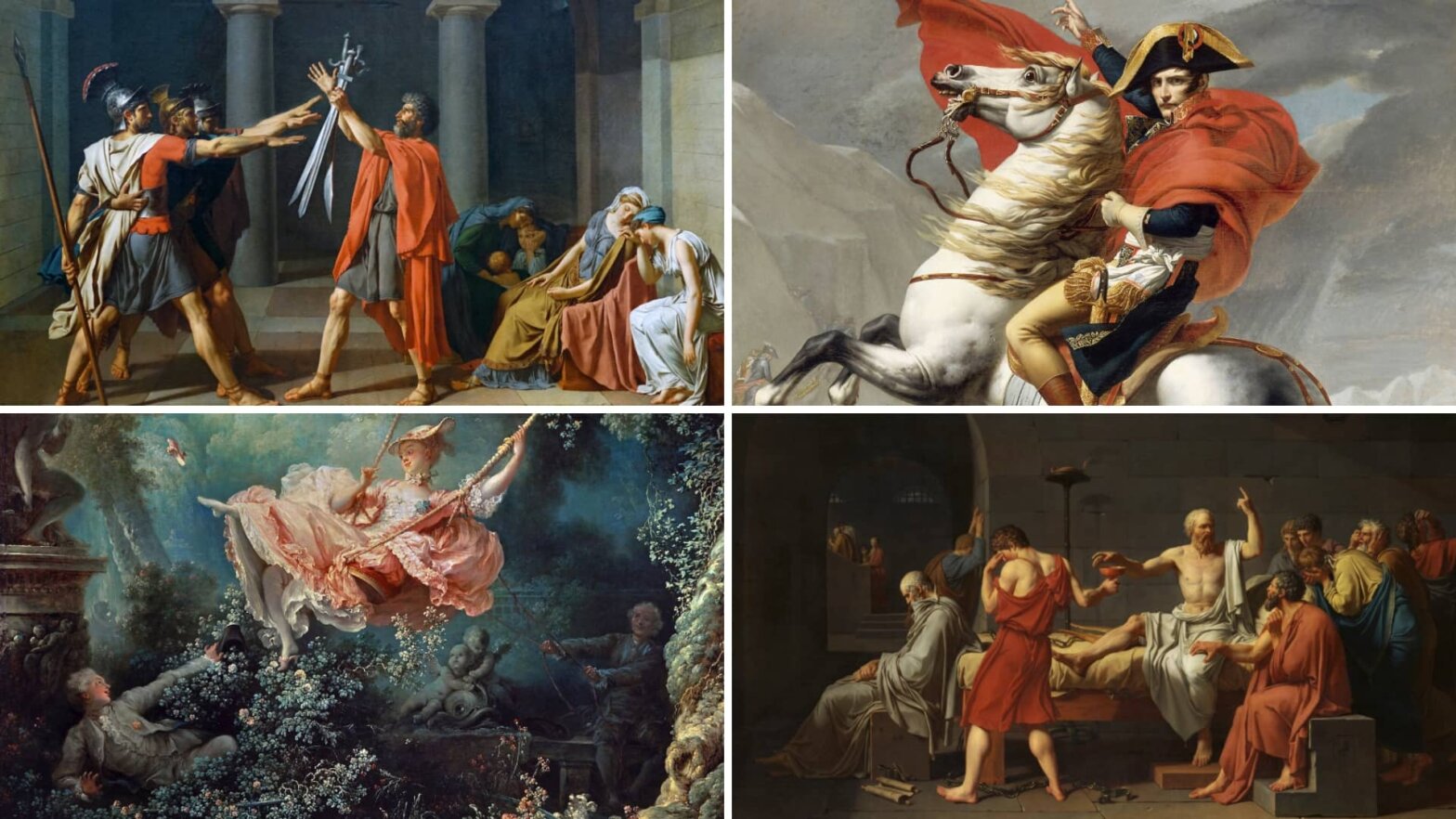
David was a French painter who's credited as a leading figure in the Neoclassical movement. David’s 1784 painting Oath of the Horatii is considered a masterpiece of the Neoclassicism style.
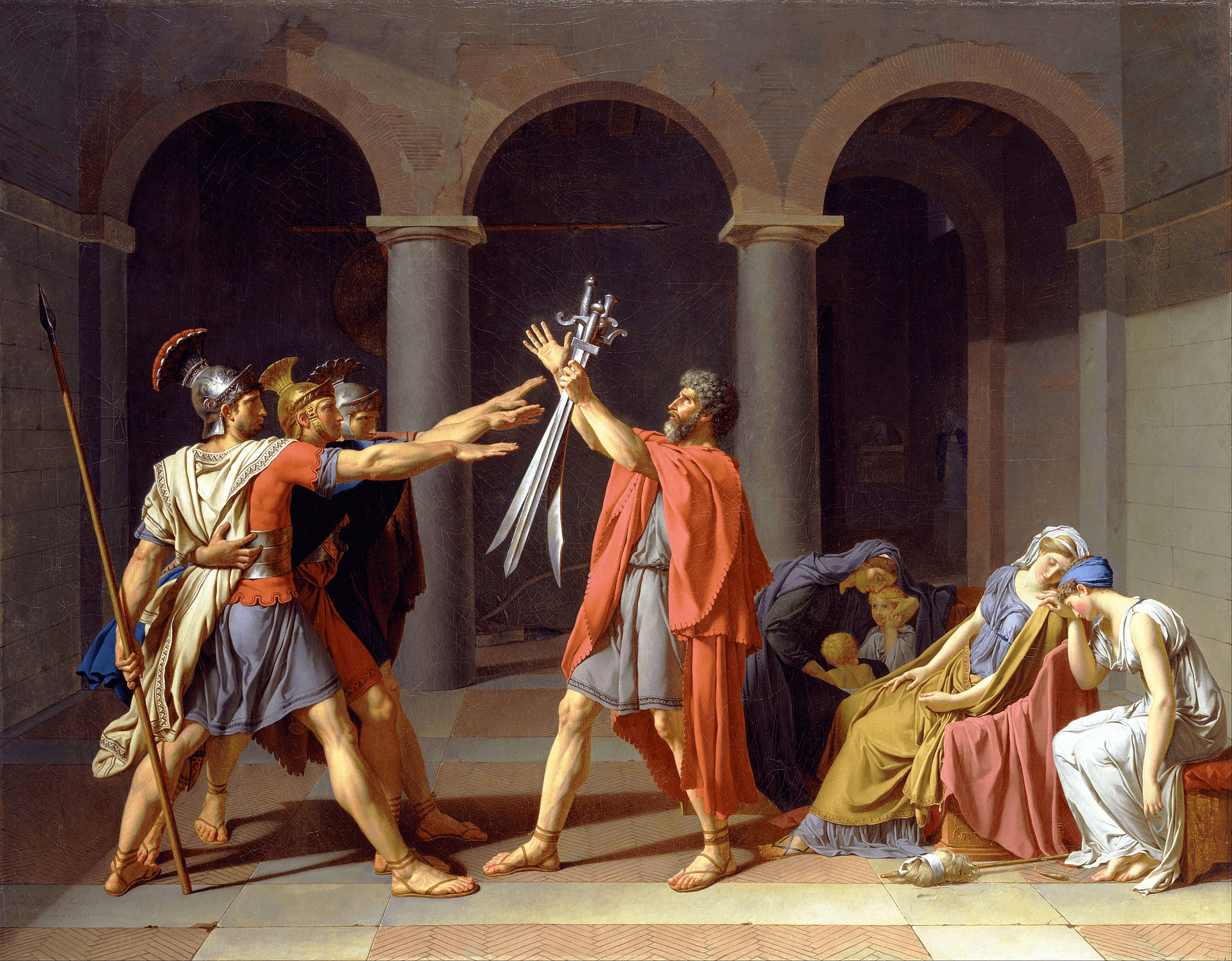
Neoclassicism Paintings • Oath of the Horatii by Jacques-Louis David
David commissioned dozens of Neoclassical works during his time as France’s resident maestro, but none were as revered as Oath of the Horatii.
Antonio Canova
Canova was an Italian sculptor and plenipotentiary of the Catholic Church. His sculpted works (most notably of which were Psyche Revived by Cupid’s Kiss and Venus Victrix) received international acclaim throughout Europe.
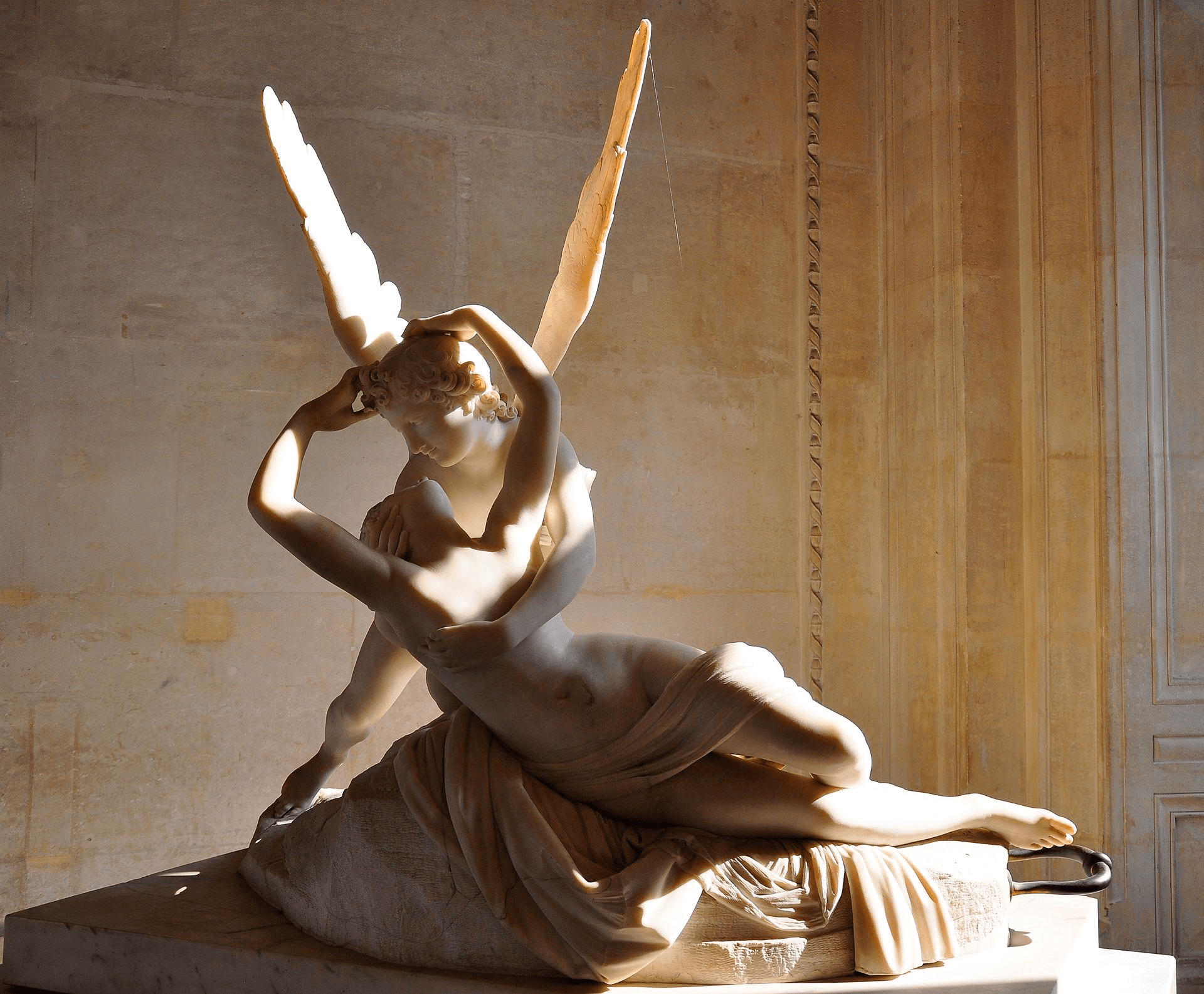
Neoclassicism Art • Psyche Revived by Cupid’s Kiss by Antonio Canova
Canova served as a European authority on Neoclassical sculpting until his death in 1822.
Angelica Kauffmann
Kauffmann was a Swiss painter and founding member of the Royal Academy. Kauffmann painted a wide breadth of subjects, including historical landscapes and portraits. Perhaps one of her most famous works was a portrait of Johann Joachim Winckelmann (as seen below).

Neoclassicism Characteristics Art • Johann Joachim Winckelmann Portrait by Angelica Kauffmann
Her legacy lives on today in the eponymous world-famous Angelika Kauffmann Museum, which is located in Schwarzenberg, Vorarlberg (Austria).
Revival of the Neoclassicism Definition
Why did Neoclassicism end?
Neoclassicism didn’t end in quite as spectacular a fashion as its predecessor, but it did diminish in popularity over time. Architecture has been perhaps the most enduring form of Neoclassicism; one which still pervades the world today.
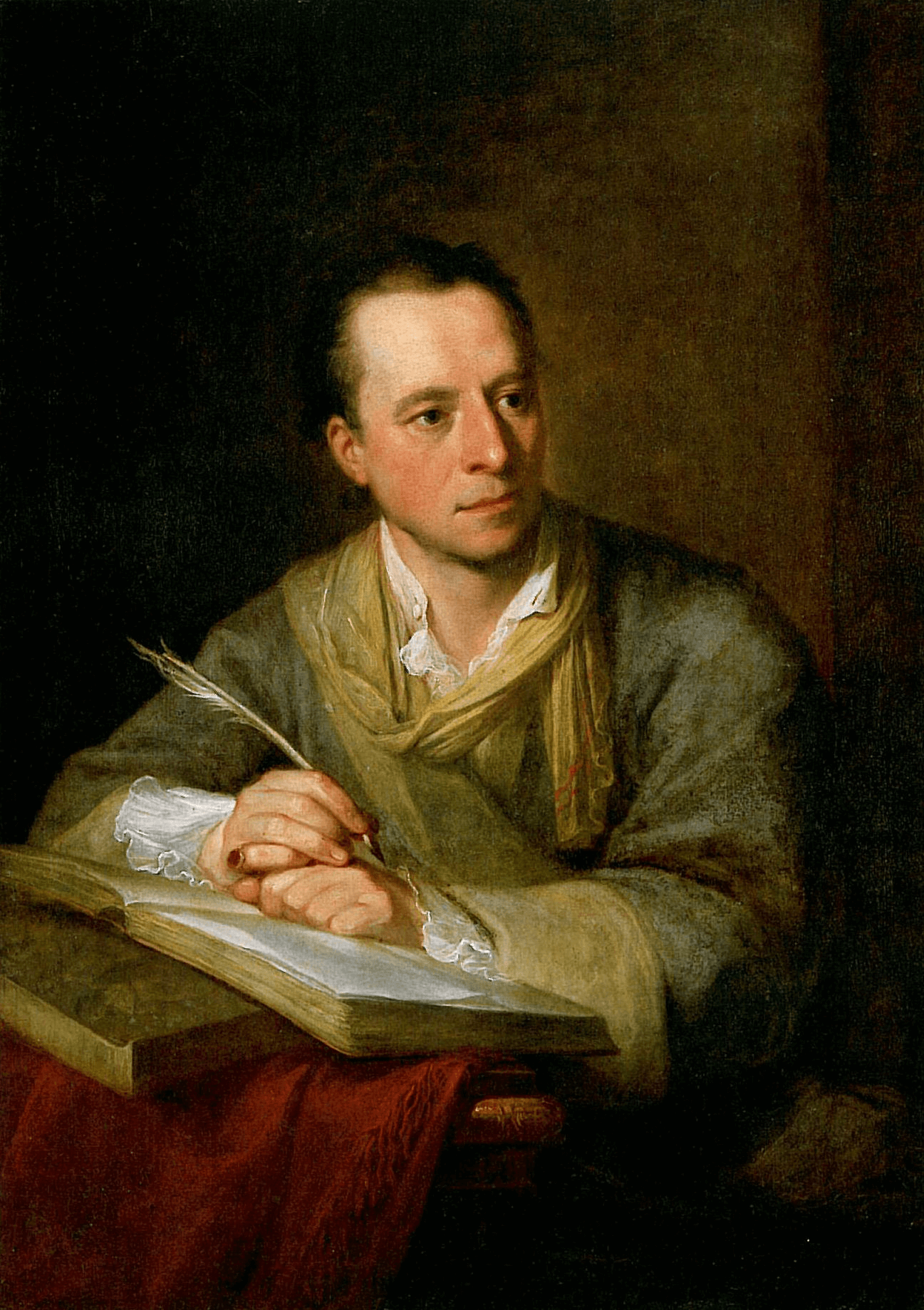
The Schermerhorn Symphony Center in Nashville, Tennessee, constructed in 2006, is a great example of the continued legacy of Neoclassical architecture.

Neoclassicism Art • Schermerhorn Symphony Center in Nashville, Tennessee
Neoclassical buildings of the 21st century have garnered the title of a “new classical style” much in the vein of the Neoclassicism style before it. But in truth there lies little distinction between the two.
Neoclassical and new classical art are both categorized by simple geometrical proportions and grandeur.
UP NEXT
Explore More Styles and Movements
This was just one of many fascinating segments of art history. There are many eras, styles, artists, and movements to discover. Let's continue our study by choosing the next stop on your way to becoming an art aficionado. Below you can visit our Art Styles Index, our Art History Timeline, or choose an individual movement.
Showcase your vision with elegant shot lists and storyboards.
Create robust and customizable shot lists. Upload images to make storyboards and slideshows.
