Empathy is more than a feeling; it’s a potent tool that allows us to understand and share the feelings of others. This capacity to connect emotionally can transform ordinary experiences into extraordinary ones. In the realms of storytelling and film, empathy has a unique role, elevating narratives and forging a deep connection between the audience and characters. This article will explore the essence of empathy and its pivotal role in creating compelling stories and memorable cinematic experiences.
What is Empathy in Storytelling?
First, let’s define empathy
Having set the stage for the importance of empathy, let's delve deeper and start by understanding its true definition.
EMPATHY DEFINITION
What is empathy?
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person. It involves placing oneself in another's shoes, and experiencing their emotions, perspectives, and situations as if they were your own. Unlike sympathy, which is feeling compassion for someone else's hardship, empathy is a more profound connection because it involves a shared perspective and emotional experience.
Empathy in storytelling, then, is how an audience is able to connect with the characters. This process is what endears us to the characters, their plight, and to ideally root for their success. Not every story needs empathetic characters but empathy remains a cornerstone of storytelling.
Characteristics of Empathy:
- Understanding and sharing another person's feelings
- Ability to see the world from others' perspectives
- Responding with compassion and sensitivity
What is Empathy in Story?
Types of empathy
Empathy is more than understanding another's perspective; it involves genuinely feeling their emotions and experiences. It goes beyond acknowledging someone else's situation to actively resonate with their joys, sorrows, fears, and hopes as if they were our own.
Let's delve into the different types of empathy that we often experience. There are three primary types of empathy that psychologists identify, these are: Cognitive, Emotional, and Compassionate.
Cognitive Empathy
Cognitive Empathy, also known as perspective-taking, is about understanding someone else's thoughts and emotions at an intellectual level. It involves recognizing what another person is feeling and thinking, allowing us to communicate effectively and provide useful advice.
Emotional Empathy
Emotional Empathy, also referred to as affective empathy, involves sharing the feelings of another person. This type of empathy allows us to emotionally respond to the joy or distress of others, creating a deeper emotional connection.
Compassionate Empathy
Compassionate Empathy, sometimes called empathic concern, goes one step further than the other two types. It involves not only understanding and sharing someone's feelings but also being moved to help, if needed. This form of empathy motivates altruistic behavior and drives us to take action to relieve another person's suffering.
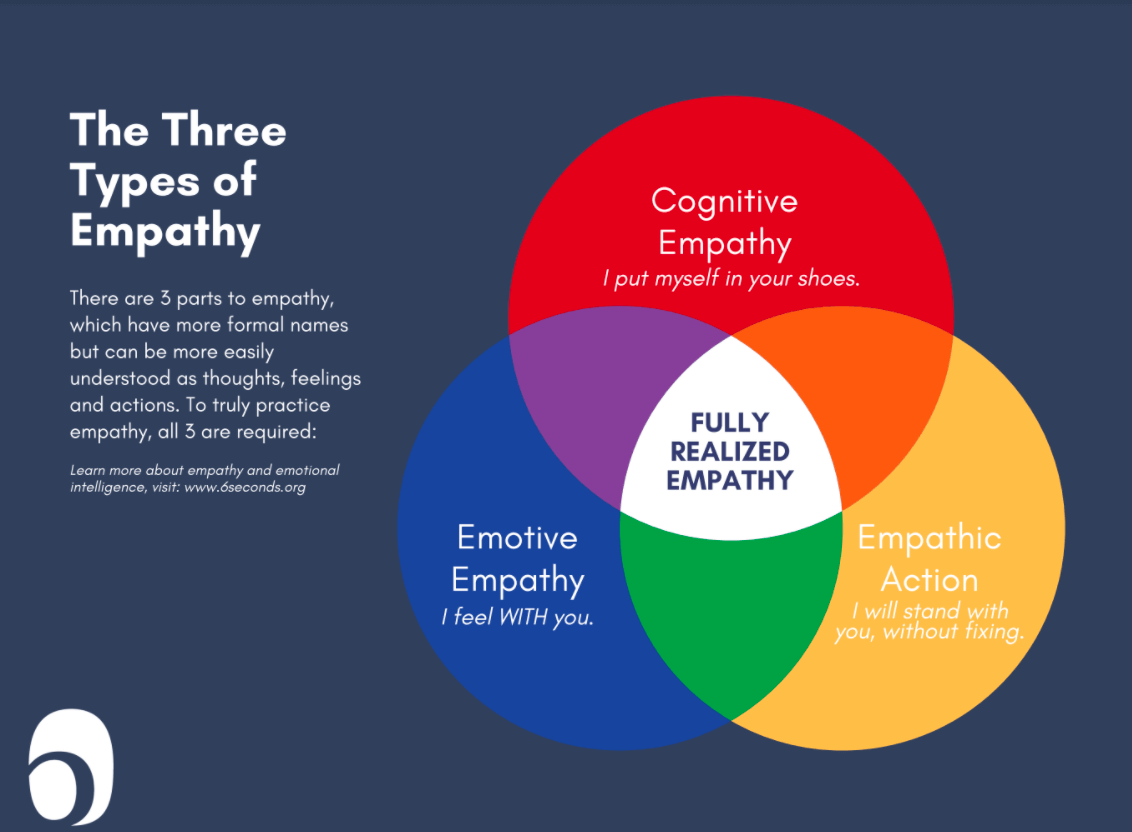
Three Types of Empathy
Empathy plays a pivotal role in human interactions as it fosters understanding, facilitates communication, and strengthens relationships. It allows us to perceive the world from different perspectives, enhancing our ability to collaborate and cooperate with others.
Empathy is developed and nurtured through various experiences and learning processes, including socialization, education, and personal experiences, which help us to understand and share the feelings of others more deeply.
Related Posts
What is Empathy Used For in Writing?
Empathy in storytelling
Empathy transforms stories from mere entertainment into immersive experiences that reflect our shared humanity, making empathy not just important, but crucial to compelling storytelling.
It is vital in storytelling as it forms the emotional bridge between the audience and the characters, making narratives resonate on a deeper level.
It allows audiences to connect and understand their motivations, and become emotionally invested in their journeys. By evoking empathy, stories can transport us into diverse worlds and experiences, making us care about the outcomes and feel a sense of shared humanity.
Character Development
Empathy allows writers to create complex, relatable characters whose thoughts, feelings, and experiences resonate with audiences. It aids in developing character arcs and helps audiences understand their motivations.
Pixar Storytelling Rules #3: Character Empathy
Human Experience
Empathy in storytelling captures the spectrum of human experiences, representing diverse perspectives and cultures. It invites audiences to step into different characters' shoes, fostering understanding and compassion. A great example of this can be found in the psychological story of Good Will Hunting.
In this breakdown by Lessons from the Screenplay, you will see how we connect to the character and catharsis of Will through his trauma despite our lack of experience with his personal trauma.
Good Will Hunting • The Psychology of Character
This immersion broadens worldviews and deepens appreciation for shared emotions and experiences. By enabling recognition of familiar emotions in varied contexts, empathy enriches narratives and promotes a deeper grasp of our multifaceted human experience.
Emotional Engagement
Empathy creates an emotional connection between audiences and characters. It makes audiences care about what happens to the characters, enhancing their emotional engagement with the story.
Narrative Depth
Empathy in storytelling allows for a deeper exploration of complex emotions and themes, enhancing the narrative's richness. It equips writers to portray characters' inner experiences authentically, moving beyond surface-level plot lines to delve into intricate emotional landscapes.
In this video analysis, Lessons from the Screenplay breaks down Nightcrawler and how the writing creates empathy for an otherwise unlikeable protagonist.
Nightcrawler • Empathy for the Antihero
This process adds depth to the story, making each moment emotionally charged and significant. Ultimately, empathy transforms narratives into meaningful reflections of life, adding profound depth by resonating with the shared human experience.
Audience Connection
Empathy forms a bridge between the story and the audience, making the audience feel seen and understood. It transforms storytelling from one-way communication into an interactive experience.
Empathy in storytelling is powerful, enabling narratives to delve into deep emotional landscapes and reflect diverse human experiences. It enriches the narrative, broadening viewers' perspectives and deepening their appreciation for shared experiences.
Empathy fosters a sense of connection and shared humanity, promoting a deeper understanding of our multifaceted human experience.
Up Next
How to Write Stronger Characters
As we've explored, empathy in storytelling allows audiences to connect deeply with diverse human experiences. But how can we harness this empathy to create compelling characters that audiences will relate to and remember? Let's dive into that in our next article, where we'll explore techniques for crafting multidimensional characters that resonate with audiences.
